Related Links
New Dwarf Planet Named Eris New! A Tenth Planet? Or just Eight? (from 2005)The Flap Over Pluto (from 1999) Sedna (from 2004)How the Planets and Satellites Got Their NamesBasic Planetary DataThe Solar System
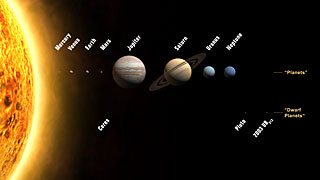
Pluto is Out!
Pluto’s new classification is “dwarf planet,” while the eight planets remaining—Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are planets. The dwarf planet definition mirrors the planet definition in the first two conditions. The third condition says that the object has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit, and the fourth states that it is not a satellite. A dwarf planet does not meet the third condition of a planet, but it must meet a fourth: a dwarf planet cannot be a satellite. As a result, Pluto’s satellite Charon, briefly considered as a full-fledged planet in the solar system, is back to being a moon. The term “pluton” was rejected and the name for this class will be decided upon in the future.
Others Considered for “Planethood”
The asteroid Ceres (classified a planet when first discovered in the 1800s) and Eris (previously nicknamed “Xena”), both formerly under consideration for planetary status, are now out. Ceres and Eris have joined Pluto as dwarfs. The IAU also has a dozen candidate planets awaiting future designation as dwarf planets, including Sedna, Orcus, Quaoar, Varuna, Ixion—all found beyond Pluto; the asteroids Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea; and four yet unnamed bodies (2003 EL61, 2005 FY9, 2002 TX300, and 2002 AW197). Also defined was “Small Solar System Bodies” as all other objects except satellites orbiting the Sun. These include the asteroids, Trans-Neptunian Objects, comets and other small bodies.